
After losing the outermost electron, it gets stable electronic configuration of the noble gas (Ne: 2, 8 ), Similarly, magnesium can lose two outermost electrons to form Mg2+ ions and aluminium can lose its three outermost electrons to form A l 3 + ion.

For example, sodium metal can lose outermost one electron to form positively charged ions, N a +. Therefore, the metal atoms can easily lose their outermost electrons to from positively charged ions. These outermost electrons are loosely held by their nuclei. The atoms of the metals have usually 1, 2 or 3 electrons in their outermost shells.
.png)
But carbon, phosphorous, sulphur etc, can be present in some alloys. (A mixture made by combining two or more metals) Non-metals are soluble event without chemical reaction and reobtained by evaporation. But if a metal dissolves, it does by reacting chemically with the solution. Usually metals are insoluble in water or other solvents. (Ability to mould into shapes and sheets without breaking) They are sonorous (make sound when struck). Possess no metallic luster and cannot be polished.Įxception : Sodium, potassium, mercury and leadĮxception : Diamond (hardest substance known)Įxception : Sodium, potassium, gallium, mercury The metalloids form a border diagonal line, separating metals from non-metals, as shown below:ģ.3 Physical Properties of Metals and Non-metalsĮxception : Bromine is a liquid. Position in the periodic table: In the periodic table, metals are placed on the left hand side and in the centre, whereas non-metals are placed on the right hand side with the exception of hydrogen, which is placed with metals on the extreme left. Among the total elements discovered, approximately 80% of them are metals and the remaining are either non-metals or metalloids. There is yet another group of elements which shows characteristics of both metals and non-metals. On the basis of their general characteristics, they are broadly divided into two major groups: (i) Metals and (ii) Non-metals. There are more than 100 elements known today. This was followed by the Bronze Age and the Iron Age. This is the reason why this period was called the Copper Age. Then man came across copper and this was the first metal man started using extensively.
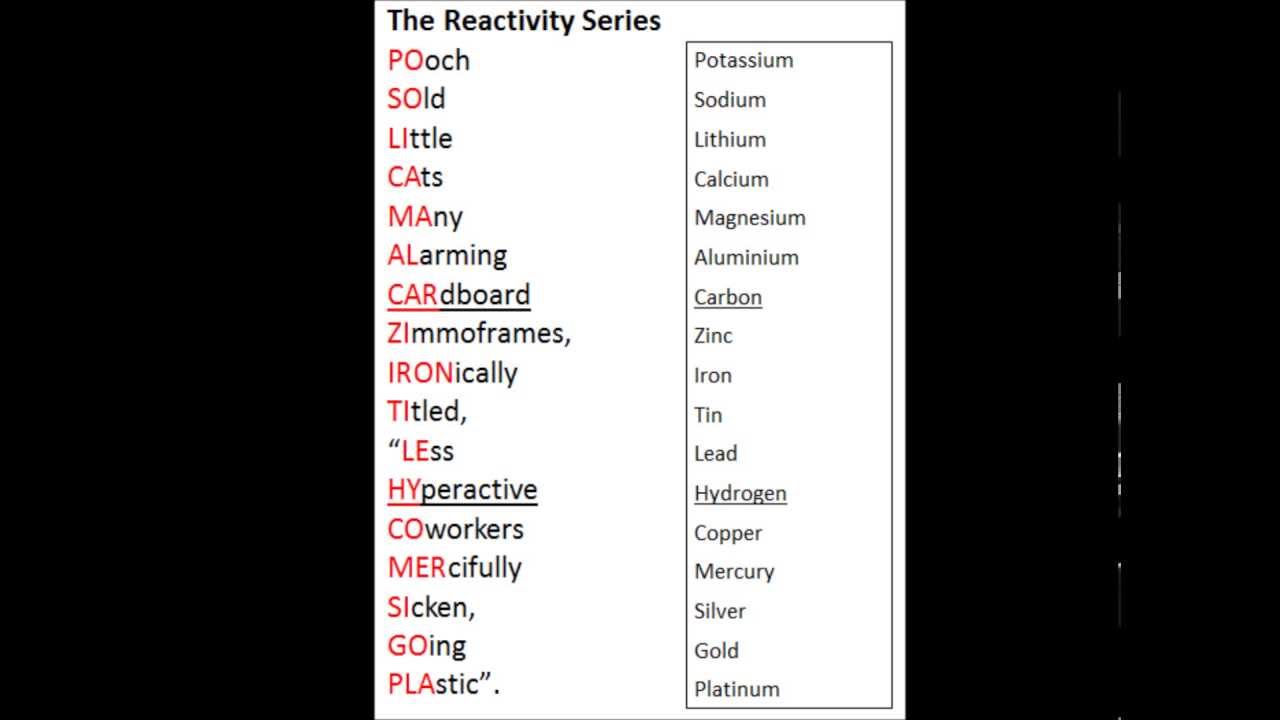
#CATION REACTIVITY SERIES FREE#
Initially, man became familiar with those metals which were occurring free in nature, like gold and copper. Man’s friendship with metals dates from prehistoric times.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
